Structured Query Language (SQL) is a simple declarative programming language utilized by various technology and business professionals to extract and transform data. Due to its versatility for storing information in both structured and unstructured formats, PostgreSQL is the fourth most used standard in modern database management systems (DBMS) worldwide1.
Nevertheless, composing even the simplest queries can require time and thought, and issues with syntax and compatibility can make this task complex, which is why many users prefer utilizing graphical user interface (GUI) tools over the traditional method of command-line interface (CLI) tools.
Despite the enduring role of CLIs for database administration and backend software engineering for lightweight (low-memory usage) scripting and automation at scale with greater control, GUIs nevertheless reduce mental work by simplifying the structure of the tasks and making their results visible to lower the barrier of entry for less technically oriented professionals for analyzing databases2.
Benefits of a GUI in Database Management
The following are the solutions to the problems with CLIs that GUIs bring3:
- Reducing the high degree of memorization and training needed to apply the syntax of the terminal commands by providing an intuitive visual interface.
- Offering comprehensive access to files, software features, and the operating system in a more user-friendly manner to ensure control.
- Providing windows to streamline multitasking through programs and file structures.
- Facilitating remote access to other computers or servers with easier navigation.
- Enabling keyboard shortcuts and possessing visual appeal and transparency to minimize strain on wrists and eyesight to prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and visual impairment from developing in users.
To conclude, GUIs are a vital addition to ease the lives of database users and developers.
When deciding which PostgreSQL GUI software product to deploy, software developers, database administrators (DBAs), and information technology (IT) managers should consider the following factors:
Core Features and Advanced Capabilities
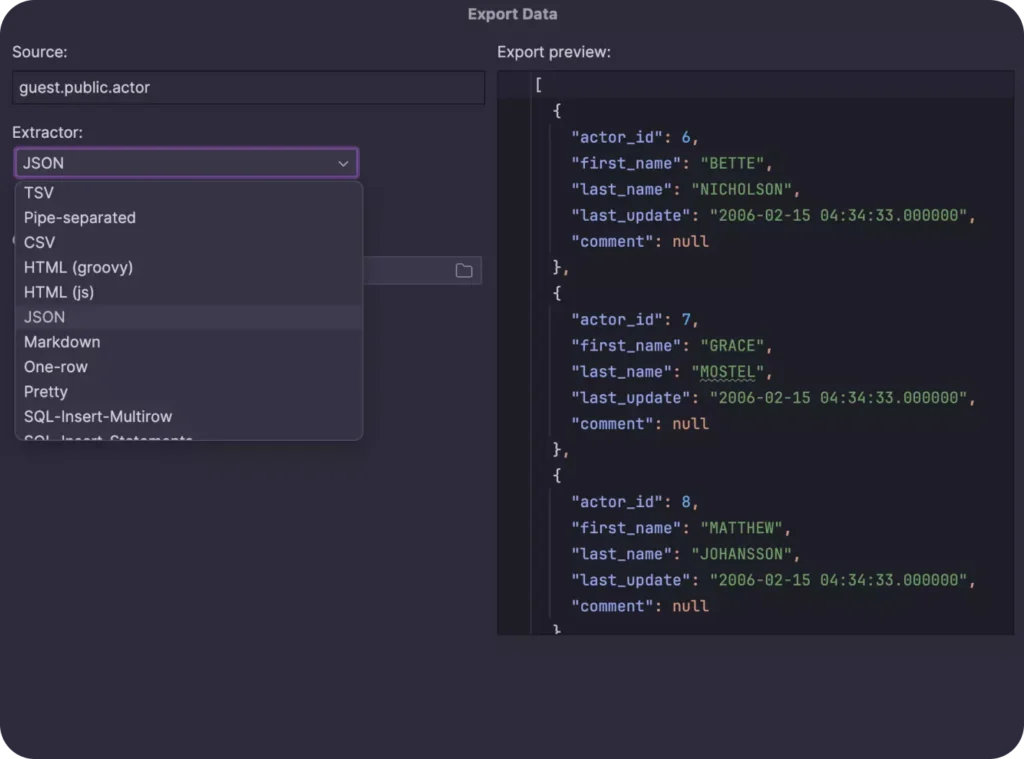
- Data Import/Export: Are there options to easily import/export data in different formats (CSV, JSON, Excel, etc.)?
- Database Management: Does the tool allow for database creation, user management, backups, restores, and schema visualization?
- Query Builder: Does the tool offer a powerful SQL editor with syntax highlighting, autocomplete, and query history?
- Advanced Features: Does the tool support stored procedures, triggers, indexing, and performance analysis?
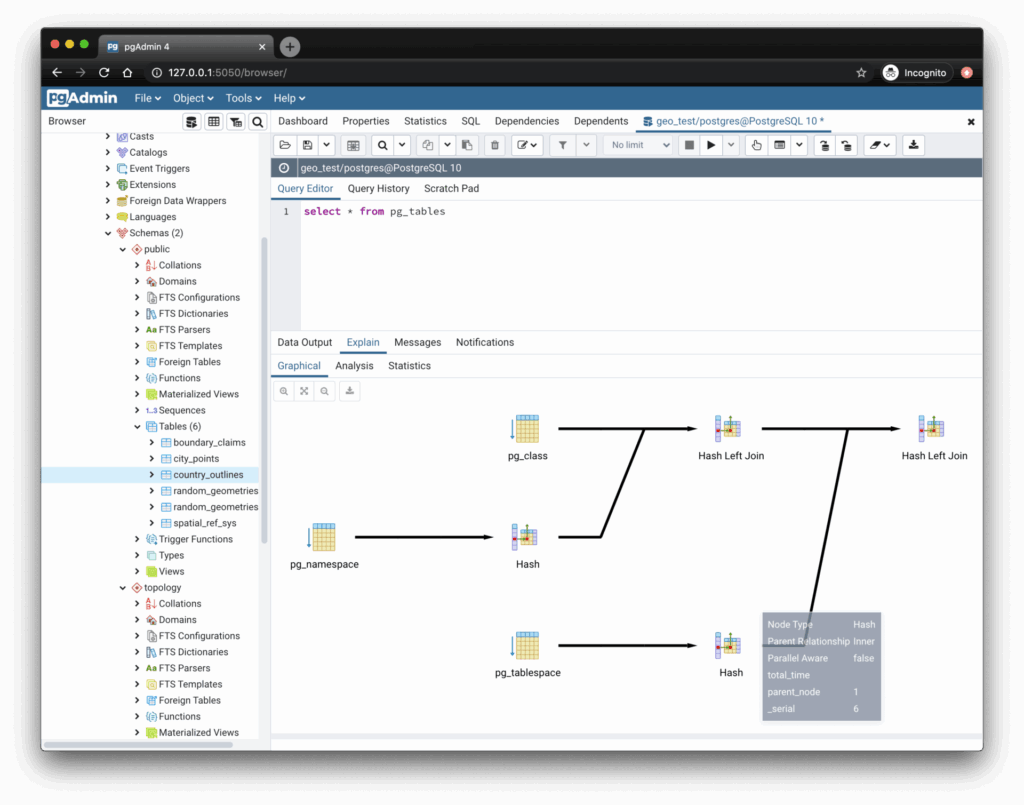
- Visualization & Reporting: Can the tool generate reports or visual representations like ER diagrams, data charts, or query execution plans?
- Audit Logging: Does the tool offer database auditing features to track changes, user activity, and access logs for compliance purposes?
User Experience and Platform Support
- Intuitiveness: Is the interface user-friendly and easy to navigate? Is it simple enough for beginners while still robust for advanced users?
- Customization: Can users customize the interface to suit their workflow (e.g., themes, layouts, font size)?
- Error Handling: Does the tool provide clear, actionable error messages when something goes wrong?
- Learning Resources: Are there tutorials, guides, and comprehensive documentation available for the tool?
- Web-Based or Desktop: Does the tool offer both desktop and web-based versions for flexible access, particularly in remote or cloud environments?
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Is the tool available on multiple operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux)?
Licensing, Security, and Support
- Free vs. Paid: Is the tool free, open-source, or does it require a license or subscription? Evaluate if the cost is justified by the features offered.
- Free Trial: Does the paid product offer a free trial so users can test before committing?
- User Authentication: Does the tool support Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Secure Shell (SSH) tunneling, or other secure authentication methods?
- Encryption: Does it allow for encrypted connections such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) between the tool and the database?
- Support and Maintenance: Does the tool come with professional support, or is it community-driven? Paid tools often offer better customer support.
- Community Support: For open-source tools, is there an active community for troubleshooting and support?
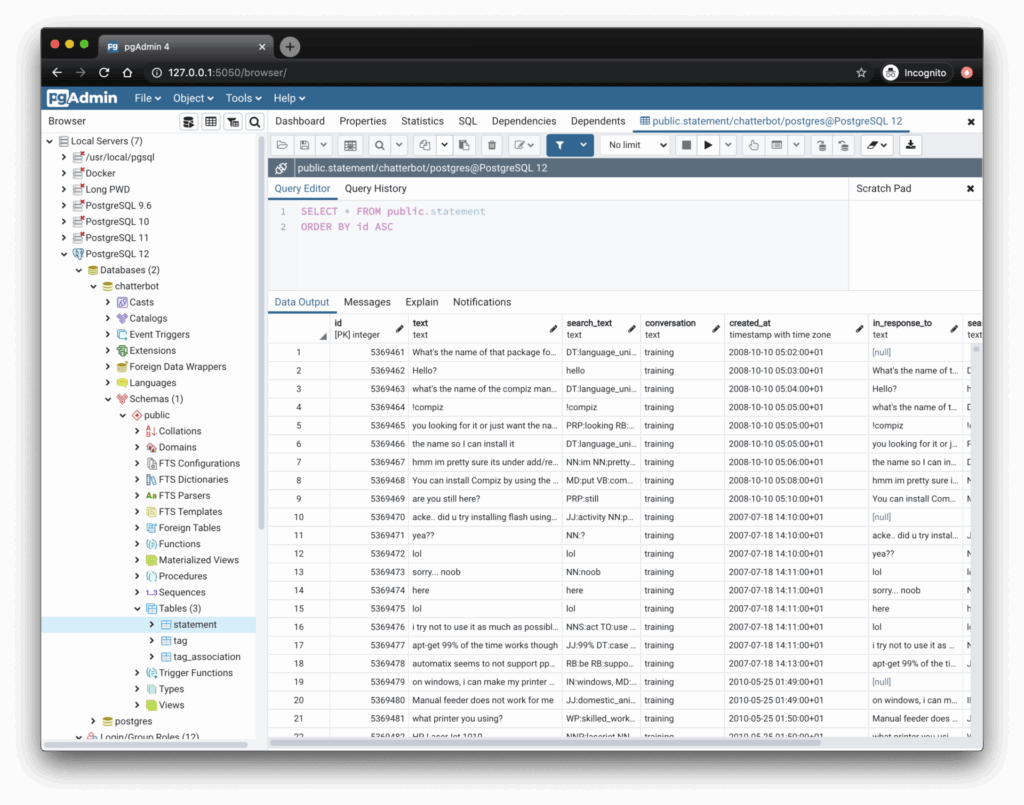
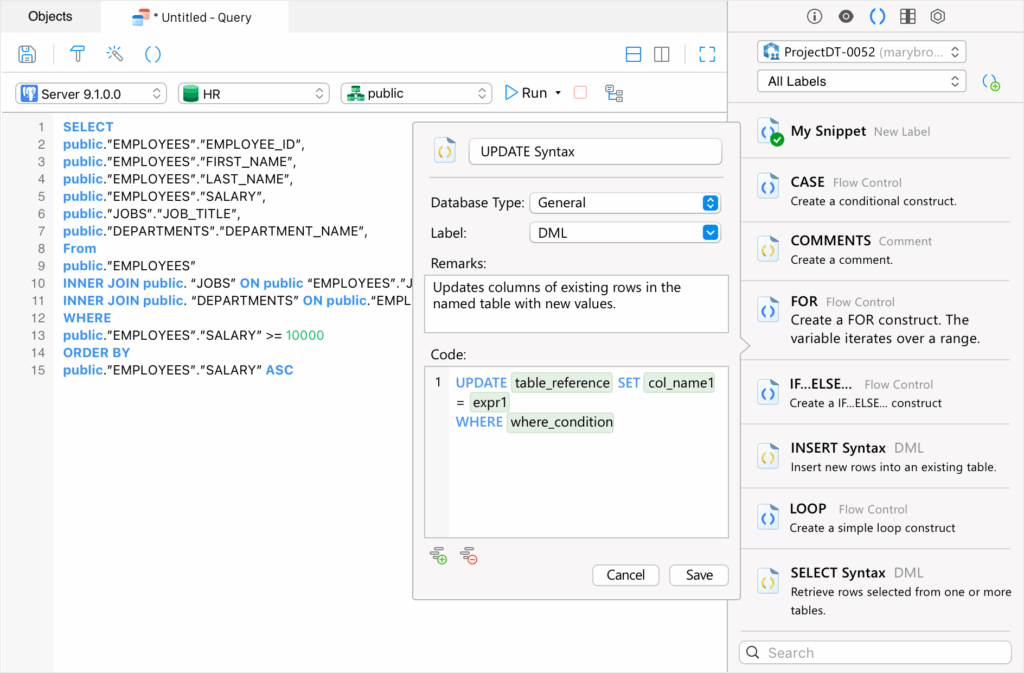
pgAdmin
pgAdmin4 is the official PostgreSQL GUI tool, offering a comprehensive suite for database management. Since it is free and open source, it has emerged as one of the most popular choices among DBAs and developers, from entry-level to experienced, and enterprises at all scales.
Features:
- A simple interface with detachable and customizable panels for managing databases, users, and roles.
- A powerful graphical query editor with syntax highlighting and autocomplete, with advanced debugging and query execution plans.
- A dashboard for monitoring activities such as database locks, connected sessions, and prepared transactions for multiple servers.
- Cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux), a web application for remote access, and a portable version for transferring data between machines.
Pros:
- Free and open source with excellent community support
- A comprehensive feature set for database administration.
Cons:
- Slow performance when handling large datasets or complex queries.
- Outdated feel of interface compared to paid and/or modern alternatives.
Pricing:
- Free: All features included.
- Paid: No paid versions.
Use Case:
- Small teams working specifically with Postgres databases preferring a free, reliable, and feature-rich open-source solution.
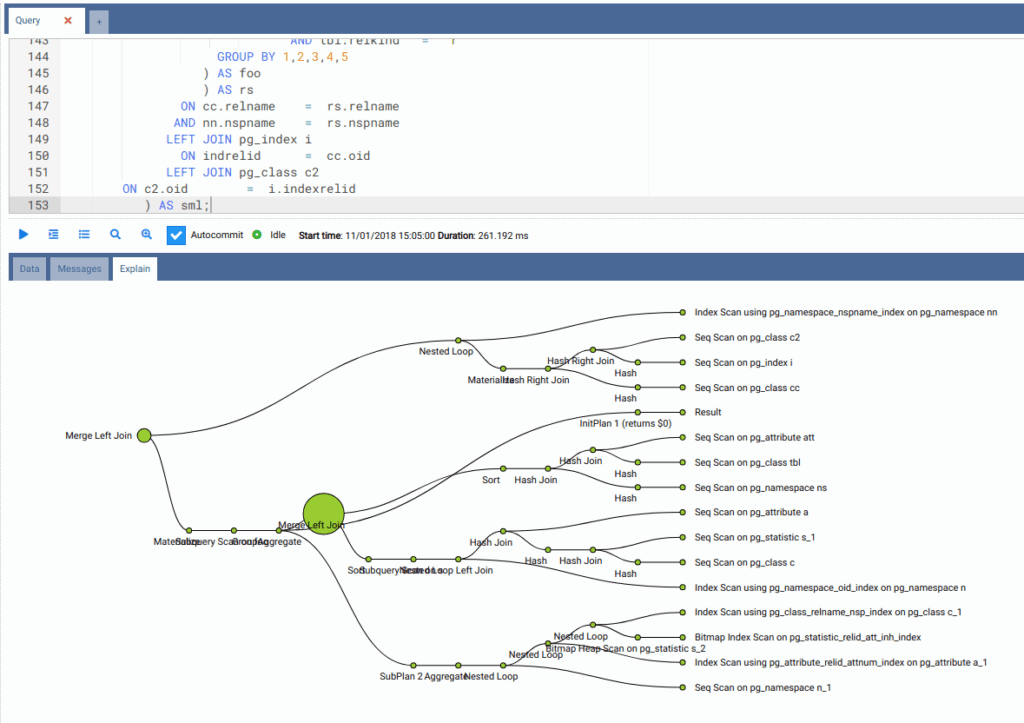
DBeaver
DBeaver5 is an open-source tool providing comprehensive database management for PostgreSQL and more than 80 other database types including popular ones such as Oracle SQL, MySQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. It is known for its flexibility and large feature set, as well as supporting databases utilizing a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) driver, rendering it a default tool for both DBAs and developers.
Features:
- A strong visual graphical query editor with syntax highlighting and autocomplete, facilitating complex queries without any knowledge of SQL required.
- A database debugger tool specifically for PostgreSQL.
- Convenience navigation among data with multiple views supported.
- The ability to generate synthetic data for system testing.
- Metadata search among rows of database tables.
- The capability to import and export data in many file formats such as CSV, XML, Microsoft Excel (XLSX), and JSON.
- The option to store passwords for multiple databases protected by a master password.
- Automatically generated entity-relationship (ER) diagrams for database schema.
- Data visualization and analytics tools with a direct integration with Tableau are possible.
Pros:
- Support for multiple database types beyond PostgreSQL.
- Open source with a thriving third-party dependency development ecosystem.
- Easy to use and highly customizable.
- Cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Capable of connecting to databases with SSH and SSL encryption.
Cons:
- Slow performance when handling large datasets or complex queries.
- Overwhelming for beginners due to its extensive feature set.
- Some advanced features being locked behind the paid version.
Pricing:
- Free: The community edition includes most features.
- Lite: $11/month or $110/year subscription.
- Enterprise: $25/month or $250/year subscription.
- Ultimate: $500/year subscription
Use Case:
- Enterprise teams working specifically with multiple types of databases requiring a unified solution for diverse environments.
DataGrip
DataGrip6 is a premium cross-platform integrated development environment (IDE) from JetBrains, a leader in this industry known for popular tools such as PyCharm and IntelliJ. It offers extensive features aimed at DBAs and developers who need deep insights.
Features:
- An aesthetic and customizable interface with a well-designed console tracking all activities and enabling the user to modify data rows with its powerful editor offering database schema navigation between tables, views, and procedures.
- An intelligent query editor with code refactoring, autocomplete, error detection, optimization, and analysis tools sensitive to context and aware of schema.
- Built-in version control (Git integration).
- ER diagrams and database modeling tools.
Pros:
- Powerful query editor with intelligent code completion.
- Integrated version control for database scripts.
- Cross-database support for multi-database projects.
- Cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux).
Cons:
- Resource-intensive, which can slow performance on lower-end machines.
- Steeper learning curve for beginners.
- Not native to PostgreSQL, lacking its specific features.
Pricing:
- Free: Only academic, open-source, and recognized developer users.
- Individual: $9.90/month or $99/year subscription.
- Organizations: $22.90/month or $220/year subscription.
Use Case:
- Enterprise teams working with multiple database types in large, complex environments requiring advanced query optimization and schema management tools.
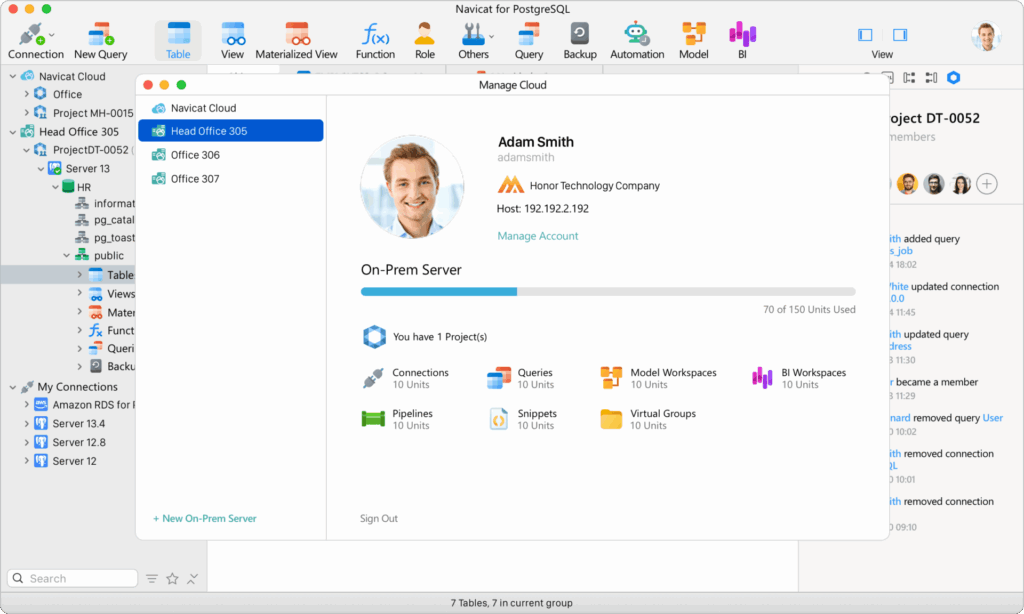
Navicat for PostgreSQL
Navicat for PostgreSQL7 is a standalone product available for sale separately from the multi-database Navicat Premium package published by PremiumSoft. It is a premium database management and development tool known for its user-friendly interface and is particularly popular among enterprise teams seeking advanced management, visualization, and migration features.
Features:
- An intuitive and fast interface with a visual query builder having code snippets and auto-completion.
- A powerful data modeling tool for visualizing and modifying database structures.
- The ability to run scheduled jobs with email notifications.
- Data synchronization and database migration tools.
- An additional cloud feature facilitating project-based team collaboration.
- Secure, stable, and reliable connections through SSH, HTTP Transfer, and SSL/TSL (Transport Security Layer).
- The capability to import and export data in many file formats such as CSV, XML, Microsoft Excel (XLSX), and JSON.
- Cloud database support and integration.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface suited for beginners.
- Strong focus on data migration and synchronization.
- Cloud support for managing remote databases.
- Excellent customer support.
- Cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux), including the Navicat Cloud service compatible with Apple iOS devices such as the iPad or iPhone.
Cons:
- Expensive compared to open-source alternatives and forces the user to be locked into a single platform for only one type of database, unless additional products, such as Navicat for MySQL are purchased piecemeal, if not the entire Navicat Premium Suite.
- Lacks some advanced coding and debugging tools available in other products.
- Has many features which may prove challenging for beginners.
Pricing:
- Free: Only 14-day trial.
- Non-Commercial: $9.99/month or $99.99/year subscription. $199 perpetual license.
- Standard: $14.99/month or $149.99/year subscription. $299 perpetual license.
- Enterprise: $22.99/month or $229.99/year subscription. $449 perpetual license.
Use Case:
- Enterprise teams requiring powerful database migration and cloud integration tools for managing multiple PostgreSQL instances across cloud environments.
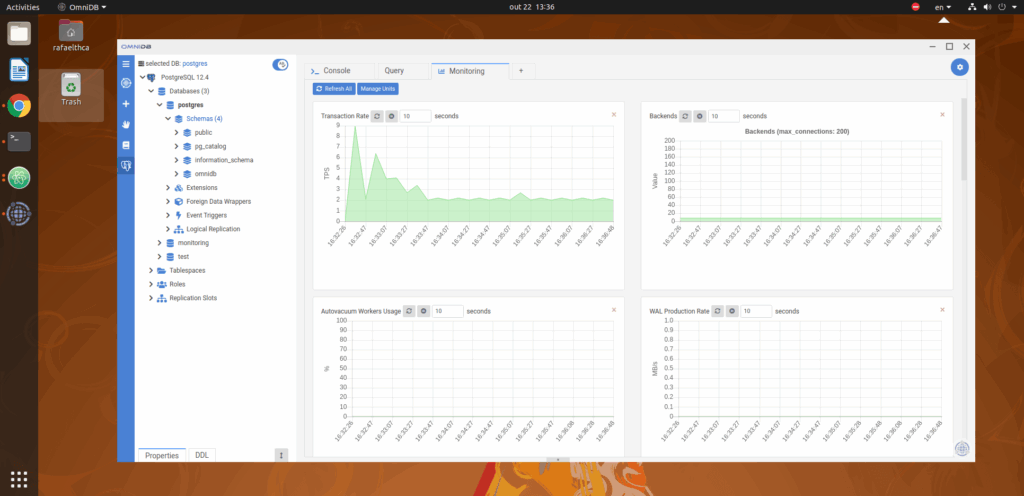
OmniDB
OmniDB8 is an open-source, database management tool built in JavaScript designed for PostgreSQL and other relational databases. Its lightweight, browser-based interface make it a popular choice for users preferring flexibility and remote access without the need to install desktop applications.
Features:
- Built in JavaScript and therefore accessible from any browser.
- A smart SQL editor with autocomplete and syntax highlighting.
- A visual query builder and data visualization tools.
- Connections to databases through encrypted channels.
- Compatibility for multiple database types beyond PostgreSQL.
- Plugins added by developers for new features, including debugging capabilities for PostgreSQL functions and procedures.
Pros:
- Free and open source.
- Browser-based to provide remote database management.
- Lightweight and simple.
- Active community for support.
Cons:
- Lack of the same level of community support compared to other open-source projects such as pgAdmin and DBeaver.
- Lack of features compared to paid desktop application products such as Datagrip and Navicat.
- Limited to basic database management tasks and lacking advanced features such as query optimization and version control.
- Requires installation through forking its GitHub repository through an operating system terminal CLI as opposed to a downloadable executable file, which is a challenge for beginners.
Pricing:
- Free: All features included.
- Paid: No paid versions.
Use Case:
- Small teams requiring a lightweight, browser-based database management tool, especially for remote access to databases without the need for a desktop application.
| pgAdmin | DBeaver | DataGrip | Navicat | OmniDB | |
| Core Features & Capabilities | Data Import / Export: CSV, JSON
Database creation, backups
Powerful SQL editor |
Data Import / Export: CSV, Excel, JSON
Database creation, user management
SQL editor with autocomplete |
Data Import / Export: Limited formats
Schema visualization, database management Intelligent SQL editor |
Data Import / Export: CSV, JSON, XML
Database management, schema visualization SQL editor with autocomplete |
Data Import / Export: Basic CSV
Limited database management
SQL editor with autocomplete |
| Advanced Features & Reporting | Stored procedures, triggers
ER diagrams
No audit logging |
Stored procedures, triggers, indexing
ER diagrams
No audit logging |
Advanced query analysis
ER diagrams
No audit logging |
Data migration, cloud integration
ER diagrams, query reports
Audit logging included |
Basic query builder
No advanced features or reporting No audit logging |
| User Experience | Simple interface
Customizable
Clear error handling |
Customizable
Overwhelming for beginners Clear error messages |
Highly customizable
Steep learning curve Helpful error detection |
Very user-friendly
Highly customizable Clear error messages |
Lightweight interface
Not customizable
Simple error messages |
| Platform Support | Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux)
Web-based access |
Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux)
No web-based access |
Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux)
No web-based access |
Cross-platform (Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS)
Web-based access available |
Browser-based only |
| Licensing & Security | Free
SSL encryption
No MFA support |
Freemium
SSH, SSL encryption MFA (Enterprise) |
Paid
SSH, SSL encryption No MFA |
Paid
SSL, SSH encryption MFA supported |
Free
SSL encryption
No MFA |
| Support & Community | Excellent community
No professional support |
Active community
Professional support in paid versions |
Professional support
Limited community for free users |
Excellent professional support
Small but active community |
Limited community support
No professional support |
How to Choose a PostgreSQL GUI Tool
Selecting the most suitable PostgreSQL GUI depends on several factors, including technical expertise, team size, budget, and the specific features required.
- Technical Expertise
Beginner/Intermediate Users: If new to database management, pick a tool with a simple, intuitive interface. Tools such as pgAdmin or Navicat can be ideal due to their user-friendly design; with Navicat offering a more premium, polished experience, but at a cost. OmniDB is also good for those who need a lightweight, browser-based tool that’s easy to configure beyond having to install it from its GitHub repository.
Advanced Users: If experienced with managing databases and needing more advanced features like stored procedures, performance analysis, and SQL debugging; tools such as DataGrip or DBeaver offer comprehensive query building and data management capabilities. These tools provide deeper control over query operations but come with a steeper learning curve.
- Team Size
Small Teams: For smaller teams or solo developers, free and open-source tools such as pgAdmin or OmniDB offer more than enough functionality for routine database management. They are lightweight and scalable, and do not require a significant financial investment.
Medium to Large Teams: As teams grow, they may require more collaborative features, professional support, and advanced functionality. DBeaver (Enterprise Edition / Ultimate Edition) and Navicat provide robust team collaboration features, such as shared projects, cloud integration, and synchronization across team members.
Enterprise Teams: For larger, enterprise-level teams dealing with complex databases, Navicat and DataGrip are well-suited. They offer advanced database management, migration tools, and support for multiple database types, making them ideal for larger, distributed teams.
- Budget Constraints
Free/Open-Source Solutions: If budget is a primary concern, pgAdmin and OmniDB are excellent free options. Both are open source, offering solid PostgreSQL management capabilities without any cost.
Freemium/Low-Cost Solutions: DBeaver offers a free community edition with the option to upgrade to paid versions for more advanced features. This makes it a good option for small to medium teams looking for flexibility in scaling up without a large upfront cost.
Paid Solutions: Navicat and DataGrip are paid tools, with Navicat offering a variety of subscription models depending on the level of features needed. If budget allows, these tools provide the powerful data management, migration, and collaboration features ideal for teams that need robust professional support and premium functionalities.
- Need for Specific Features
Data Import/Export: If frequent data migrations, imports, or exports are crucial, tools like DBeaver and Navicat offer robust data import/export capabilities in multiple formats (CSV, JSON, Excel). These tools also support cloud integration, making it easier to manage remote databases.
Advanced Query and Performance Analysis: For users who need powerful query optimization tools, DataGrip and DBeaver (Enterprise Edition / Ultimate Edition) are standout choices. They come with features such as query analysis, performance monitoring, and advanced SQL refactoring capabilities.
Collaboration: If a team requires real-time collaboration and cloud access, Navicat provides built-in cloud integration, allowing team members to work simultaneously on the same projects, with features such as version control and shared schema designs.
Security and Compliance: For environments that demand high security, DBeaver (Enterprise Editions / Ultimate Edition) and Navicat support advanced encryption methods such as SSL or SSH as well as MFA. pgAdmin and OmniDB also offer SSL encryption for secure database connections, although they lack MFA support.
Here’s a summary of the top tools and their best use cases:
| Tool | Best Use Cases | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| pgAdmin | Best Free Tool
Best for Small Teams |
Free, open-source, cross-platform, wide community support. | Outdated user interface, slower performance with large datasets. |
| DBeaver | Best for Versatility
Best Freemium Tool |
Multiple database support, customizable, good for medium teams. | Some advanced features behind paywall, complex for beginners. |
| DataGrip | Best for Developers
Best for Power Users |
Powerful SQL editor, multiple database support, advanced query tools. | Paid-only, steep learning curve, resource-heavy. |
| Navicat | Best for Enterprises
Best for Cloud Integration |
User-friendly, excellent cloud / database migration tools, collaboration. | Expensive compared to alternatives, lacks deep coding tools. |
| OmniDB | Best for Lightweight
Best Browser-Based |
Browser-based, free, simple user interface, easy for remote access | Limited features, lacks advanced capabilities, no executable install package. |
Recommended PostgreSQL GUIs for Specific Use Cases
| Use Case | Recommended Tool | Reason |
| Best for Enterprises | Navicat | Offers cloud integration, database migration, collaboration features, and strong customer support. |
| Best Free Tool | pgAdmin | Fully open-source, great community support, and suitable for small teams or individuals. |
| Best Freemium Tool | DBeaver | Free community version with optional paid upgrades for advanced features and multi-database support. |
| Best for Developers | DataGrip | Advanced query refactoring, deep SQL optimization, version control integration. |
| Best for Beginners | pgAdmin | Simple and intuitive interface, no cost, large online community for support. |
| Best for Versatility | DBeaver | Supports over 80 databases, highly customizable, and works across multiple platforms. |
| Best Web-Based Tool | OmniDB | Lightweight and easy-to-use for remote management through a browser, no desktop installation required. |
| Best for Cloud Integration | Navicat | Excellent cloud integration features for managing multiple remote databases. |
| Best for Small Teams | pgAdmin or OmniDB | Both tools are lightweight, free, and perfect for smaller projects with basic database needs. |
If you are working on a tight budget or starting out with PostgreSQL, pgAdmin is the go-to tool, providing a wealth of features for free. DBeaver offers an excellent balance between free and paid tiers for teams that need flexibility across multiple database environments. DataGrip is ideal for developers needing deep query analysis, while Navicat is best suited for enterprise teams prioritizing cloud integration and collaboration tools. Lastly, for a simple, browser-based tool, OmniDB is perfect for remote access and lightweight database management.
1 Taylor, Petroc. “Ranking of the most popular database management systems worldwide, as of June 2024.” Statista, 19 Jun. 2024, https://www.statista.com/statistics/809750/worldwide-popularity-ranking-database-management-systems/
2 “CLI vs GUI – Which one is better?” TablePlus, 26 Aug. 2018, https://tableplus.com/blog/2018/08/cli-vs-gui-which-one-is-better.html
3 “Command line vs. GUI.” Computer Hope.,08 Aug. 2021, https://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch000619.htm
4 “pgAdmin: PostgreSQL Tools.” pgAdmin, https://www.pgadmin.org/
5 “DBeaver Community: Free Universal Database Tool.” DBeaver, https://dbeaver.io/
6 “DataGrip: A powerful cross-platform tool for relational and NoSQL databases.” JetBrains, https://www.jetbrains.com/datagrip/
7 “Navicat for PostgreSQL.” Navicat, https://www.navicat.com/en/products/navicat-for-postgresql
8 OmniDB. “OmniDB”. GitHub, https://github.com/OmniDB/OmniDB