MongoDB® vs Cassandra
Are you considering MongoDB® vs Cassandra as the data store for your next project? Would you like to compare the two databases? Cassandra and MongoDB are both “NoSQL” databases, but the reality is that they are very different. They have very different strengths and value propositions – so any comparison has to be a nuanced one. Let’s start with initial requirements.
Neither of these databases replaces RDBMS, nor are they “ACID” databases. So If you have a transactional workload where normalization and consistency are the primary requirements, neither of these databases will work for you. You are better off sticking with traditional relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc. Now that we have relational databases out of the way, let’s consider the major differences between Cassandra and MongoDB that will help you make the decision. In this post, I am not going to discuss specific features but will point out some high-level strategic differences to help you make your choice.
1. Expressive Object Model
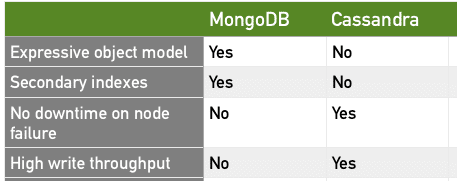
MongoDB supports a rich and expressive object model. Objects can have properties and objects can be nested in one another (for multiple levels). This model is very “object-oriented” and can easily represent any object structure in your domain. You can also index the property of any object at any level of the hierarchy – this is strikingly powerful! Cassandra, on the other hand, offers a fairly traditional table structure with rows and columns. Data is more structured and each column has a specific type which can be specified during creation.
Verdict: If your problem domain needs a rich data model, then MongoDB hosting is a better fit for you.
2. Secondary Indexes
Secondary indexes are a first-class construct in MongoDB. This makes it easy to index any property of an object stored in MongoDB even if it is nested. This makes it really easy to query based on these secondary indexes. Cassandra has only cursory support for secondary indexes. Secondary indexes are also limited to single columns and equality comparisons. If you are mostly going to be querying by the primary key then Cassandra will work well for you.
Verdict: If your application needs secondary indexes and needs flexibility in the query model then MongoDB is a better fit for you.
3. High Availability
MongoDB supports a “single master” model. This means you have a master node and a number of slave nodes. In case the master goes down, one of the slaves is elected as master. This process happens automatically but it takes time, usually 10-40 seconds. During this time of new leader election, your replica set is down and cannot take writes. This works for most applications but ultimately depends on your needs. Cassandra supports a “multiple master” model. The loss of a single node does not affect the ability of the cluster to take writes – so you can achieve 100% uptime for writes.
Verdict: If you need 100% uptime Cassandra is a better fit for you.
4. Write Scalability
MongoDB with its “single master” model can take writes only on the primary. The secondary servers can only be used for reads. So essentially if you have three node replica set, only the master is taking writes and the other two nodes are only used for reads. This greatly limits write scalability. You can deploy multiple shards but essentially only 1/3 of your data nodes can take writes. Cassandra with its “multiple master” model can take writes on any server. Essentially your write scalability is limited by the number of servers you have in the cluster. The more servers you have in the cluster, the better it will scale.
Verdict: If write scalability is your thing, Cassandra is a better fit for you.
5. Query Language Support
Cassandra supports the CQL query language which is very similar to SQL. If you already have a team of data analysts they will be able to port over a majority of their SQL skills which is very important to large organizations. However CQL is not full blown ANSI SQL – It has several limitations (No join support, no OR clauses) etc. MongoDB at this point has no support for a query language. The queries are structured as JSON fragments.
Verdict: If you need query language support, Cassandra is the better fit for you.
6. Performance Benchmarks
Let’s talk performance. At this point, you are probably expecting a performance benchmark comparison of the databases. I have deliberately not included performance benchmarks in the comparison. In any comparison, we have to make sure we are making an apples-to-apples comparison.
1. Database model – The database model/schema of the application being tested makes a big difference. Some schemas are well suited for MongoDB and some are well suited for Cassandra. So when comparing databases it is important to use a model that works reasonably well for both databases.
2. Load characteristics – The characteristics of the benchmark load are very important. E.g. In write-heavy benchmarks, I would expect Cassandra to smoke MongoDB. However, in read-heavy benchmarks, MongoDB and Cassandra should be similar in performance.
3. Consistency requirements – This is a tricky one. You need to make sure that the read/write consistency requirements specified are identical in both databases and not biased towards one participant. Very often in a number of the ‘Marketing’ benchmarks, the knobs are tuned to disadvantage the other side. So, pay close attention to the consistency settings.
One last thing to keep in mind is that the benchmark load may or may not reflect the performance of your application. So in order for benchmarks to be useful, it is very important to find a benchmark load that reflects the performance characteristics of your application. Here are some benchmarks you might want to look at:
– NoSQL Performance Benchmarks
– Cassandra vs. MongoDB vs. Couchbase vs. HBase
7. Ease of Use
If you had asked this question a couple of years ago MongoDB would be the hands-down winner. It’s a fairly simple task to get MongoDB up and running. In the last couple of years, however, Cassandra has made great strides in this aspect of the product. With the adoption of CQL as the primary interface for Cassandra, it has taken this a step further – they have made it very simple for legions of SQL programmers to use Cassandra very easily.
Verdict: Both are fairly easy to use and ramp up.
8. Native Aggregation
MongoDB has a built-in Aggregation framework to run an ETL pipeline to transform the data stored in the database. This is great for small to medium jobs but as your data processing needs become more complicated the aggregation framework becomes difficult to debug. Cassandra does not have a built-in aggregation framework. External tools like Hadoop, Spark are used for this.
Database Trends – SQL vs. NoSQL
9. Schema-less Models
In MongoDB, you can choose to not enforce any schema on your documents. While this was the default in prior versions in the newer version you have the option to enforce a schema for your documents. Each document in MongoDB can be a different structure and it is up to your application to interpret the data. While this is not relevant to most applications, in some cases the extra flexibility is important. Cassandra in the newer versions (with CQL as the default language) provides static typing. You need to define the type of very column upfront.
To summarize here are the important differences in table form: